Category:Coastal Modeling Environment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
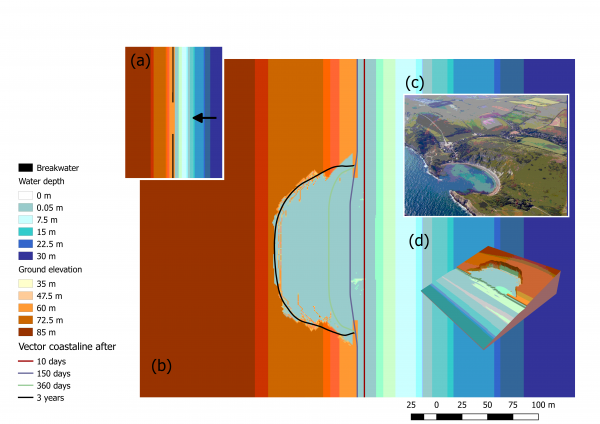
[[File:Lolworthcoveweb8a07.png|frame|alt=Numerical Simulation of Cove creation using the Coastal Modeling Environment|Simulated embayment creation on an initially rectilinear coastline. (a) At the start of the simulation, all the coastline of a gently sloping topography is protected by a breakwater but a short segment in the centre that is un-protected. (b) Location of the vector coastline at different time steps and final topography after three years of simulation. © The resulting embayment is bounded by a cliff similar to the Lulworth Cove bay in the south of the UK.]] | |||
== Metadata == | |||
=== Summary === | |||
Also known as '''CoastalME''', it is a C++ package to support the creation of numerical dynamic models to simulate coastal landscape evolution on spatial scales of kms to tens of kms, over decadal to centennial timescales. It has been designed with and for coastal engineers and practitioners seeking to simulate the interaction of multiple coastal landforms and different types of human interventions (e.g. grey and nature based solutions) to better manage the compound risk of coastal flooding and erosion. | |||
We are now working on making this an [https://www.osgeo.org/projects/coastalme/ "OSGeo Community model"]. | |||
=== Technical specs === | |||
=== In/Outputs === | |||
== | |||
=== Process === | |||
=== Testing === | |||
== History == | |||
It was first released in 2017<ref name = "Payo2017">Payo, A., Favis-Mortlock, D., Dickson, M., Hall, J. W., Hurst, M. D., Walkden, M. J. A., . . . Ellis, M. A. (2017). Coastal Modelling Environment version 1.0: a framework for integrating landform-specific component models in order to simulate decadal to centennial morphological changes on complex coasts. Geosci. Model Dev., 10(7), 2715-2740. '''Open source paper''' [https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-10-2715-2017].</ref> as a proof of concept under the NERC funded iCoast project. The initial core team of developers<ref name="Payo2017"/> described in detail the rationale behind CoastalME and demonstrated how it can be used to integrate; the Soft Cliff and Platform Erosion model SCAPE<ref name="Walkden2011">M. J. Walkden and J. W. Hall "A Mesoscale Predictive Model of the Evolution and Management of a Soft-Rock Coast," Journal of Coastal Research 27(3), 529-543, (1 May 2011). [https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00099.1]</ref>, the Coastal Vector Evolution Model COVE<ref>Hurst, M. D., Barkwith, A., Ellis, M. A., Thomas, C. W., and Murray, A. B. (2015), Exploring the sensitivities of crenulate bay shorelines to wave climates using a new vector-based one-line model, J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf., 120, 2586– 2608, [https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JF003704].</ref> and the Cross Shore model CSHORE<ref>Kobayashi, Nobuhisa. "Coastal sediment transport modeling for engineering applications." Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering 142.6 (2016): 03116001.[https://ascelibrary.org/doi/10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000347]</ref>. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
{{author | |||
|AuthorURL=https://www.bgs.ac.uk/people/payo-garcia-andres/ | |||
|AuthorFullName= Andres Payo | |||
|AuthorName= Agarcia }} | |||
[[Category:Coasts and estuaries geohazards]] | [[Category:Coasts and estuaries geohazards]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 13 February 2025
Metadata
Summary
Also known as CoastalME, it is a C++ package to support the creation of numerical dynamic models to simulate coastal landscape evolution on spatial scales of kms to tens of kms, over decadal to centennial timescales. It has been designed with and for coastal engineers and practitioners seeking to simulate the interaction of multiple coastal landforms and different types of human interventions (e.g. grey and nature based solutions) to better manage the compound risk of coastal flooding and erosion.
We are now working on making this an "OSGeo Community model".
Technical specs
In/Outputs
Process
Testing
History
It was first released in 2017[1] as a proof of concept under the NERC funded iCoast project. The initial core team of developers[1] described in detail the rationale behind CoastalME and demonstrated how it can be used to integrate; the Soft Cliff and Platform Erosion model SCAPE[2], the Coastal Vector Evolution Model COVE[3] and the Cross Shore model CSHORE[4].
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Payo, A., Favis-Mortlock, D., Dickson, M., Hall, J. W., Hurst, M. D., Walkden, M. J. A., . . . Ellis, M. A. (2017). Coastal Modelling Environment version 1.0: a framework for integrating landform-specific component models in order to simulate decadal to centennial morphological changes on complex coasts. Geosci. Model Dev., 10(7), 2715-2740. Open source paper [1].
- ↑ M. J. Walkden and J. W. Hall "A Mesoscale Predictive Model of the Evolution and Management of a Soft-Rock Coast," Journal of Coastal Research 27(3), 529-543, (1 May 2011). [2]
- ↑ Hurst, M. D., Barkwith, A., Ellis, M. A., Thomas, C. W., and Murray, A. B. (2015), Exploring the sensitivities of crenulate bay shorelines to wave climates using a new vector-based one-line model, J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf., 120, 2586– 2608, [3].
- ↑ Kobayashi, Nobuhisa. "Coastal sediment transport modeling for engineering applications." Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering 142.6 (2016): 03116001.[4]
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|
This category currently contains no pages or media.