Climate
Africa Groundwater Atlas >> Additional resources >> Supporting environmental information >> Climate
Please cite page as: Africa Groundwater Atlas. 2019. Climate. British Geological Survey. Accessed [date you accessed the information]. Weblink.
Climate of Africa
Maps and graphs that provide an overview of precipitation (rainfall) and temperature in each country in Africa over have been derived for this Atlas from data provided by the Climatic Research Unit at the University of East Anglia. For this Atlas, precipitation and temperature for the period 1951 to 2010 have been used.
Precipitation and temperature data for Africa from 1951 to 2010 were extracted from the CRU TS 3.21 dataset produced by the Climatic Research Unit at the University of East Anglia. This is a global gridded dataset of monthly observations over the period 1901–2012. The spatial resolution of the dataset is 0.5°.

The CRU TS3.21 dataset is made available to researchers for non-commercial use through the Centre for Environmental Data Archival (CEDA). Users must register with CEDA to access the dataset. Use of the data is covered by the following licence: http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3/.
Full details of how the CRU TS 3.21 dataset was developed are in Jones and Harris (2013).
Jones, P D, and Harris, I. 2013. CRU TS3.21: Climatic Research Unit (CRU) Time-Series (TS) Version 3.21 of High resolution gridded data of month-by-month variation in climate (Jan. 1901–Dec. 2012). NCAS British Atmospheric Data Centre, 24th September 2013. doi:10.5285/D0E1585D-3417-485F-87AE-4FCECF10A992. http://dx.doi.org/10.5285/D0E1585D-3417-485F-87AE-4FCECF10A992
If you reproduce any of the climate maps or graphs from this Atlas, please cite both the Africa Groundwater Atlas and the Climate Research Unit (CRU TS 3.21).
A note on climate data reliability
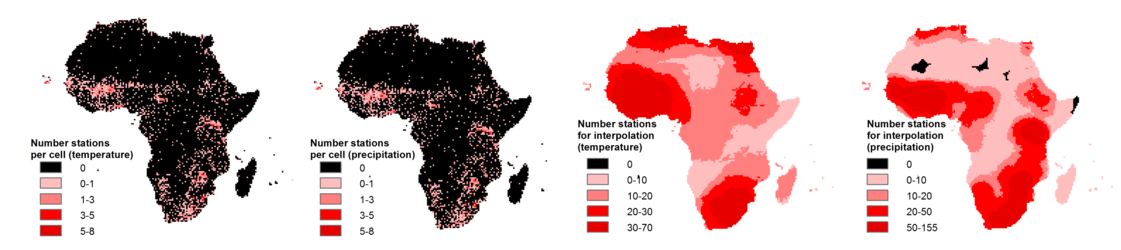
The reliability of the climate data depends on the number of climate monitoring stations providing the data used in interpolation of the gridded dataset. In some areas of Africa, there are few climate monitoring stations and they are spaced far apart; and not all stations have continuous records over time. Only data from stations which have a >75% complete record over the period 1961–1990 were used in the development of the CRU TS 3.21 dataset.
The maps below illustrate the density of climate monitoring stations across Africa, and therefore the availability of climate data. They act as a proxy to indicate the reliability of the interpolated climate dataset. In areas where there are fewer stations, the interpolated precipitatation and temperature data should be treated as less reliable than in areas where there is a higher density of stations.
The number of station observations in each grid cell at each monthly time-step have been averaged over the period 1951–2010 and are shown on the maps below. The data from each station can influence the interpolated (gridded) value in a given cell if it lies within a predefined correlation decay distance of another station: set at 450 km for precipitation data and 1200 km for temperature data. For Africa, approximately 75% of the grid cells contain station data, or have station data within the correlation decay distance, with valid values over the period 1901–2000. The number of stations used to calculate the interpolated data value at each grid cell has been averaged over all time-steps between 1951 and 2010 and is shown on the maps below.
Climate zones
Climate zones are a useful way of classifying regional climate. They are defined here based on the updated Köppen-Geiger climate classification (Peel et al., 2007), which is available to download in the supplementary material to the paper presented by Peel et al. (2007).
The Köppen-Geiger classification is a widely used scheme that has been updated using long-term station records of monthly precipitation and temperature from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN) version 2.0 dataset. Similarly with all derived datasets, the reliability of the dataset is dependent on the density of input data. Detailed information on the classification system can be found in Peel et al. (2007).
Peel, M C, Finlayson, B L, and McMahon, T A. 2007. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrology and Earth System Science, Vol. 11, 1633–1644. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007
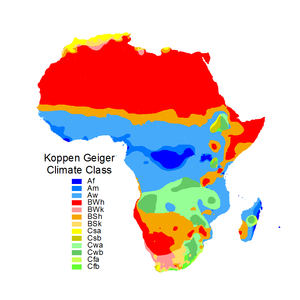
| Af | Tropical rainforest | Am | Tropical monsoon |
| Aw | Tropical savannah | ||
| BSh | Arid steppe (hot) | BSk | Arid steppe (cold) |
| BWh | Arid desert (hot) | BWk | Arid desert (cold) |
| Cfa | Temperate without dry season (hot summer) | Cfb | Temperate without dry season (warm summer) |
| Csa | Temperate with dry summer (hot summer) | Csb | Temperate with dry summer (warm summer) |
| Cwa | Temperate with dry winter (hot summer) | Cwb | Temperate with dry winter (warm summer) |
Africa Groundwater Atlas >> Additional resources >> Supporting environmental information >> Climate