Hydrogeology of Algeria: Difference between revisions
m 1 revision imported |
m Protected "Hydrogeology of Algeria" ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite)) [cascading] |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 07:24, 5 June 2015
Geographical and Political Setting

General
The majority of Algeria's land surface is dominated by the Sahara Desert. This is separated from the coastal region by the Tellian and Saharan Atlas Mountain Ranges, which run across the country from east to west, parallel to the Mediterranean coast.
| Estimated Population in 2013* | 39,208,194 |
| Rural Population (% of total)* | 30% |
| Total Surface Area* | 2,381,740 sq km |
| Agricultural Land (% of total area)* | 17% |
| Capital City | Algiers |
| Region | North Africa |
| Border Countries | Tunisia, Libya, Niger, Mali, Mauritania and Morocco |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal (2013)* | 5,723 Million cubic metres |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Agriculture* | 61% |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Domestic Use* | 24% |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Industry* | 15% |
| Rural Population with Access to Improved Water Source* | 80% |
| Urban Population with Access to Improved Water Source* | 86% |
* Source: World Bank
Climate
The climate of Algeria's northern coastal region is temperate, with dry, hot summers and mild, wet winters. Average annual precipitation in this region is around 600 mm. The climate in the south of Algeria is arid, with average annual rainfall close to zero. Average temperatures generally increase from north to south, although values are slightly higher in the coastal region compared to the Atlas mountains, because of the cooling effect of elevation.
-
Koppen Geiger Climate Zones
-
Average Annual Precipitation
-
Average Temperature
There are temporal changes in precipitation and temperature throughout the year. The hottest months of June, July and August generally correspond to a distinct dry season. Rainfall time-series and graphs of monthly average rainfall and temperature for each of the two climate zones can be found on the Algeria Climate Page.
For further detail on the climate datasets used see the climate resources section.
Surface water
| Low rainfall means that the majority of rivers in the mountainous and desert regions of Algeria are ephemeral, flowing only after large rainfall events. Only the rivers in the northern coastal region are perennial, flowing all year round.
The Chelif (or Cheliff) River is the longest river in Algeria, flowing for 700 km from its source in the Saharan Atlas to its discharge point in the Mediterranean Sea. More info from country authors...
|
 |
Soil
 |
Soils in the mountainous Atlas region of Algeria are dominated by stony Leptosols.
In the drier area to the north of the Atlas, soils are generally rich in calcium carbonate (Calcisols). Many of these soils are suitable for agriculture, but water availability is a key constraint on crop growth. Along the wetter coastal region, soils are better developed and give rise to more vegetation - these include Luvisols and Cambisols. Vertisols, which support extensive cereal cultivation and grazing, occur in the eastern coastal region of Algeria. The arid region to the south of the Atlas is characterised by poorly developed Leptosols, which contain little organic matter. Regions of Arenosols denote large areas of sand dunes. Fluvisols are found along river valleys. To the south of the Atlas the rivers are generally ephemeral, but in the wetter northern region, where rivers are perennial, the valleys are often intensively cultivated. |
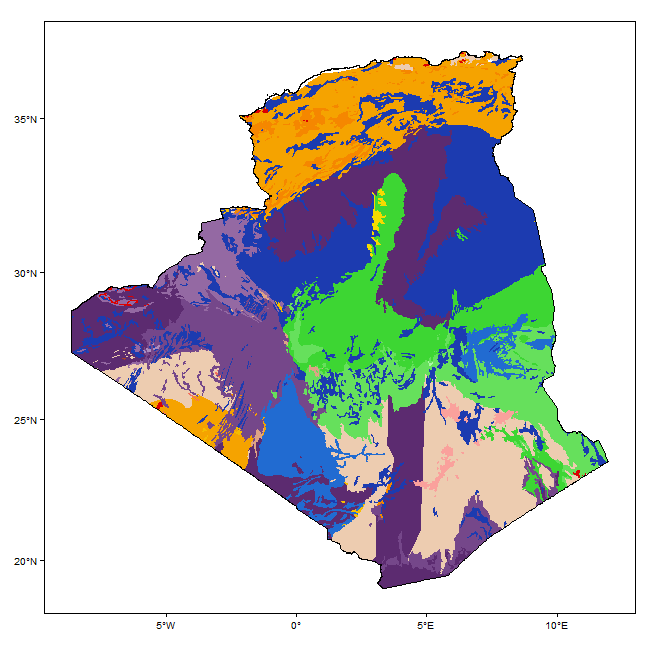
Land cover
Geology

| Key Formations | Period | Lithology | Structure |
| Unconsolidated Deposits | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 3 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 4 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Igneous | |||
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Sedimentary Basin | |||
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 3 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 4 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 5 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 6 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features
|
| Precambrian Metasedimentary | |||
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Precambrian Mobile/Orogenic Belt | |||
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Precambrian Craton | |||
| Name of Formation 1 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
| Name of Formation 2 | Geological Period | Further detail on the lithology of this formation | Important structural features |
Hydrogeology
This section will contain a broad overview of the hydrogeology.
Aquifer properties
Unconsolidated
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
Igneous
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
|}
Consolidated Sedimentary - Intergranular Flow
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
Consolidated Sedimentary - Intergranular & Fracture Flow
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
Consolidated Sedimentary - Fracture Flow
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
Basement
| Named Aquifers | General Description | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 1 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 2 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 3 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
| Aquifer 4 | General description, including properties, thickness, confined/unconfined | Water quantity issues | Water quality issues | Recharge |
Groundwater Status
General information on groundwater quantity, groundwater quality, river-aquifer interaction and groundwater dependent ecosystems.
Groundwater use and management
Groundwater use
Overview of groundwater use.
Groundwater management
Overview of groundwater management.
Transboundary aquifers
Overview of transboundary aquifers.
Groundwater monitoring
Overview of groundwater monitoring.